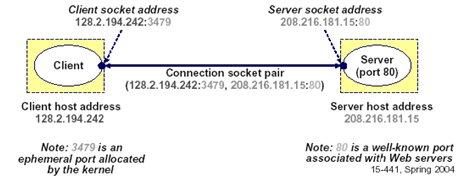
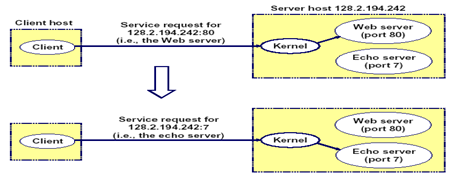
Pengertian Teori Komputasi
Teori komputasi adalah cabang ilmu komputer dan matematika yang membahas apakah dan bagaimanakah suatu masalah dapat dipecahkan pada model komputasi, menggunakan algoritma. Bidang ilmu ini terutama membahas hal terkait komputabilitas dan kompleksitas, dalam kaitannya dengan formalisme komputasi.
Untuk melakukan studi komputasi dengan ketat, ilmuwan komputer bekerja dengan abstraksi matematika dari komputer yang dinamakan model komputasi. Ada beberapa model yang digunakan, namun yang paling umum dipelajari adalah mesin Turing.
Untuk melakukan studi komputasi dengan ketat, ilmuwan komputer bekerja dengan abstraksi matematika dari komputer yang dinamakan model komputasi. Ada beberapa model yang digunakan, namun yang paling umum dipelajari adalah mesin Turing.
Sebuah mesin Turing dapat dipikirkan sebagai komputer pribadi meja dengan kapasitas memori yang tak terhingga, namun hanya dapat diakses dalam bagian-bagian terpisah dan diskret. Ilmuwan komputer mempelajari mesin Turing karena mudah dirumuskan, dianalisis dan digunakan untuk pembuktian, dan karena mesin ini mewakili model komputasi yang dianggap sebagai model paling masuk akal yang paling ampuh yang dimungkinkan. Kapasitas memori tidak terbatas mungkin terlihat sebagai sifat yang tidak mungkin terwujudkan, namun setiap permasalahan yang "terputuskan" (decidable) yang dipecahkan oleh mesin Turing selalu hanya akan memerlukan jumlah memori terhingga. Jadi pada dasarnya setiap masalah yang dapat dipecahkan (diputuskan) oleh meisn Turing dapat dipecahkan oleh komputer yang memiliki jumlah memori terbatas.
Pengertian Komputasi Modern
Komputasi modern bisa disebut sebuah konsep sistem yang menerima intruksi-intruksi dan menyimpannya dalam sebuah memory, memory disini bisa juga dari memory komputer. Oleh karena pada saat ini kita melakukan komputasi menggunakan komputer maka bisa dibilang komputer merupakan sebuah komputasi modern. Konsep ini pertama kali digagasi oleh John Von Neumann (1903-1957). Dalam kerjanya komputasi modern menghitung dan mencari solusi dari masalah yang ada, dan perhitungan yang dilakukan itu meliputi :
1. Akurasi
2. Kecepatan
3. ProblemVolume Besar
4. Modelling
5. Kompleksitas
1. Akurasi
2. Kecepatan
3. ProblemVolume Besar
4. Modelling
5. Kompleksitas
Sejarah Komputasi Modern
John von Neumann (1903-1957) adalah ilmuan yang meletakkan dasar-dasar komputer modern. Dalam hidupnya yang singkat, Von Neumann telah menjadi ilmuwan besar abad 21. Von Neumann meningkatkan karya-karyanya dalam bidang matematika, teori kuantum, game theory, fisika nuklir, dan ilmu komputer. Beliau juga merupakan salah seorang ilmuwan yang sangat berpengaruh dalam pembuatan bom atom di Los Alamos pada Perang Dunia II lalu.
Von Neumann dilahirkan di Budapest, Hungaria pada 28 Desember 1903 dengan nama Neumann Janos. Dia adalah anak pertama dari pasangan Neumann Miksa dan Kann Margit. Di sana, nama keluarga diletakkan di depan nama asli. Sehingga dalam bahasa Inggris, nama orang tuanya menjadi Max Neumann. Pada saat Max Neumann memperoleh gelar, maka namanya berubah menjadi Von Neumann. Setelah bergelar doktor dalam ilmu hukum, dia menjadi pengacara untuk sebuah bank. Pada tahun 1903, Budapest terkenal sebagai tempat lahirnya para manusia genius dari bidang sains, penulis, seniman dan musisi.
Von Neumann juga belajar di Berlin dan Zurich dan mendapatkan diploma pada bidang teknik kimia pada tahun 1926. Pada tahun yang sama dia mendapatkan gelar doktor pada bidang matematika dari Universitas Budapest. Keahlian Von Neumann terletak pada bidang teori game yang melahirkan konsep seluler automata, teknologi bom atom, dan komputasi modern yang kemudian melahirkan komputer. Kegeniusannya dalam matematika telah terlihat semenjak kecil dengan mampu melakukan pembagian bilangan delapan digit (angka) di dalam kepalanya.
Setelah mengajar di Berlin dan Hamburg, Von Neumann pindah ke Amerika pada tahun 1930 dan bekerja di Universitas Princeton serta menjadi salah satu pendiri Institute for Advanced Studies.
Dipicu ketertarikannya pada hidrodinamika dan kesulitan penyelesaian persamaan diferensial parsial nonlinier yang digunakan, Von Neumann kemudian beralih dalam bidang komputasi. Sebagai konsultan pada pengembangan ENIAC, dia merancang konsep arsitektur komputer yang masih dipakai sampai sekarang. Arsitektur Von Nuemann adalah komputer dengan program yang tersimpan (program dan data disimpan pada memori) dengan pengendali pusat, I/O, dan memori. (dna).
Von Neumann dilahirkan di Budapest, Hungaria pada 28 Desember 1903 dengan nama Neumann Janos. Dia adalah anak pertama dari pasangan Neumann Miksa dan Kann Margit. Di sana, nama keluarga diletakkan di depan nama asli. Sehingga dalam bahasa Inggris, nama orang tuanya menjadi Max Neumann. Pada saat Max Neumann memperoleh gelar, maka namanya berubah menjadi Von Neumann. Setelah bergelar doktor dalam ilmu hukum, dia menjadi pengacara untuk sebuah bank. Pada tahun 1903, Budapest terkenal sebagai tempat lahirnya para manusia genius dari bidang sains, penulis, seniman dan musisi.
Von Neumann juga belajar di Berlin dan Zurich dan mendapatkan diploma pada bidang teknik kimia pada tahun 1926. Pada tahun yang sama dia mendapatkan gelar doktor pada bidang matematika dari Universitas Budapest. Keahlian Von Neumann terletak pada bidang teori game yang melahirkan konsep seluler automata, teknologi bom atom, dan komputasi modern yang kemudian melahirkan komputer. Kegeniusannya dalam matematika telah terlihat semenjak kecil dengan mampu melakukan pembagian bilangan delapan digit (angka) di dalam kepalanya.
Setelah mengajar di Berlin dan Hamburg, Von Neumann pindah ke Amerika pada tahun 1930 dan bekerja di Universitas Princeton serta menjadi salah satu pendiri Institute for Advanced Studies.
Dipicu ketertarikannya pada hidrodinamika dan kesulitan penyelesaian persamaan diferensial parsial nonlinier yang digunakan, Von Neumann kemudian beralih dalam bidang komputasi. Sebagai konsultan pada pengembangan ENIAC, dia merancang konsep arsitektur komputer yang masih dipakai sampai sekarang. Arsitektur Von Nuemann adalah komputer dengan program yang tersimpan (program dan data disimpan pada memori) dengan pengendali pusat, I/O, dan memori. (dna).
Teori Automata & Bahasa Formal
- Otomata
- Bahasa Formal
Finite State Machine (Mesin Status Terhingga)
Dapat digunakan untuk memodelkan suatu alat untuk mengenali (menerima) kalimat-kalimat di dalam suatu bahasa. Selain itu juga dapat digunakan untuk memodelkan suatu sistem fisik seperti vending machine. Ciri-ciri:
- Memiliki himpunan terhingga dari status-status, S = {s0, s1, s2, …}
- Unsur khusus berupa s0 yaitu status awal dalam himpunan S
- Himpunan masukan terhingga, I = {i0, i1, i2, …}
- Himpunan keluaran terhingga, O = {o0, o1, o2, …}
- Memiliki fungsi transisi
- Memiliki fungsi keluaran
Mesin Turing
Seorang matematikawan asal Inggris bernama Alan Turing
mengusulkan suatu model sederhana yang memiiliki kemampuan komputer yakni general-purpose pada tahun 1936. Mesin turing
dapat digunakan untuk menghitung kelas fungsi bilangan bulat yang dikenal
sebagai fungsi rekursif parsial.
Komponen mesin turing:
- Pengendali status terhingga (finite state control)
- Pita masukan yang bersifat:
a. Panjangnya
tak terhingga (dari ujung kiri ke ujung kanan)
b. Dapat
dibaca dan ditulis
Pada keadaan awal n sel
pertama dari pita masukan berisi rangkaian simbol yang harus dikenali. Sel-sel
lain di sebelah kanan rangkaian simbol berisi simbol kosong. Perilaku mesin Turing tergantung pada simbol masukan di
posisi kepala (head). Aksi yang dapat
dilakukan yaitu:
- Berubah status
- Menuliskan simbol pada sel pita masukan. Aksi ini akan mengubah simbol yang sebelumnya berada pada sel ttersebut.
- Menggerakkan head ke kiri atau kanan.
Notasi formal mesin Turing : M = (Q, Ʃ, г, δ, q0, B, F)
Dimana:
Q = himpunan terhingga dari status
Ʃ = subset dari г, termasuk di dalamnya B, yang merupakan
himpunan dari simbol-simbol masukan.
Г = himpunan terhingga dari simbol yang muncul
δ = fungsi pergerakan
yang merupakan pemetaan dari A x Г ke Q x Г x {L,R}2
q0 = status awal
B = anggota Г, melambangkan simbol spasi (blank)
F = himpunan status akhir
Sumber :